Edge Computing for Smart Systems and the Internet of Things
Optimize IoT system performance and costs with edge computing.
Digital transformation and the Internet of Things (IoT) are introducing unprecedented scalability and performance challenges for network, storage and system architects. Vast numbers of smart devices—sensors, wearables, autonomous machines, connected vehicles—are generating an ever-increasing variety, volume and velocity of data that must be processed and analyzed quickly, reliably and cost-effectively.
Traditional centralized system architectures, where data is backhauled to and processed in a central enterprise data center or in the cloud, can’t meet the increased scalability and performance demands of the digital age. Many enterprises and service providers are moving to decentralized system architectures that push certain data processing functions to the edge of the network to accelerate application performance and contain costs.
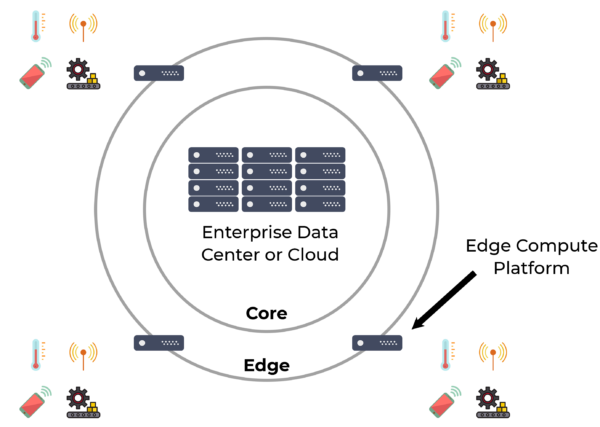
Edge Computing Improves IoT System Performance, Reliability and Economics
New edge compute gateways and servers aggregate, process and analyze data at the periphery of the enterprise or service provider network, providing a variety of functional and financial benefits.
Edge computing can help:
- Improve the performance and scalability of intelligent systems by offloading certain data collection, processing and analysis functions from applications running in the cloud.
- Accelerate the performance of delay-sensitive local applications (e.g. real-time factory-floor automation) by analyzing data locally and avoiding wide-area network (WAN) latency.
- Contain network costs by reducing upstream traffic across WAN links (and mobile backhaul networks in communications service provider scenarios).
- Extend the resiliency and survivability of smart systems by distributing compute functions across the network and eliminating single points of failure.
- Enable simpler, less-expensive IoT devices by shifting endpoint processor and memory capacity to edge gateways and servers.
Edge Computing
The delivery of computing capabilities to the logical extremes of a network in order to improve the performance, operating cost and reliability of applications and services. By shortening the distance between devices and the cloud resources that serve them, and also reducing network hops, edge computing mitigates the latency and bandwidth constraints of today’s Internet, ushering in new classes of applications.
In practical terms, this means distributing new resources and software stacks along the path between today’s centralized data centers and the increasingly large number of devices in the field, concentrated, in particular, but not exclusively, in close proximity to the last mile network, on both the infrastructure side and the device side.
Edge Computing Market Trends
Businesses in every industry are introducing edge computing to improve operational efficiencies and support smart system, IoT and big data initiatives.
In a 2018 Futurum Research Edge Computing Survey of over 500 companies:
- 73% have already implemented or are in the process of implementing an edge computing strategy.
- 72% believe their edge strategy is either critically or very important to improve business processes and productivity.
- 64% are already combining edge computing and data center analytics.
Grand View Research expects global edge computing spending to exceed $3.24 billion by 2025 as businesses and service providers move to decentralized system architectures. A large vendor ecosystem is emerging to serve this growing market, as shown below.
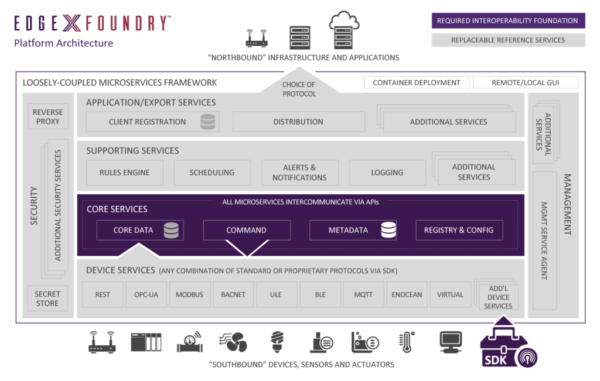
And standards-based edge compute frameworks like the Linux Foundation EdgeX Foundry project are emerging to help accelerate edge compute adoption and promote multi-vendor interoperability.
Edge Computing in an IoT System Architecture
Edge computing allows data from Internet of Things devices, sensors and applications to be analyzed and acted upon locally before it is transmitted upstream to an enterprise data center or the cloud. The diagram below shows how edge computing elements fit into a generalized IoT system reference architecture. Key system components include:
Things
Intelligent endpoints and connected devices that generate data and may require control.
Edge Gateways
Intermediate edge devices that aggregate data, control endpoints and translate protocols (e.g. convert legacy operational technology protocols like SCADA to standard IP protocols).
Edge Servers
Edge compute elements that process and analyze local data. Edge servers perform real-time analytics, execute local business logic and filter out data that has no intrinsic historic value or global significance.
Cloud/Data Center Apps
The business applications and services running in the enterprise data center or in the cloud. Examples include business intelligence, data analytics and visualization tools used by data scientists, business users and technical professionals.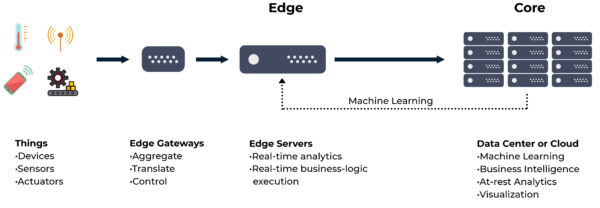
Simplified IoT System Reference Architecture
Factory-Floor Edge Compute Example
A simple manufacturing example illustrates the function of each system component. In this scenario, legacy factory-floor machines are monitored and controlled as part of smart manufacturing system, as shown below.
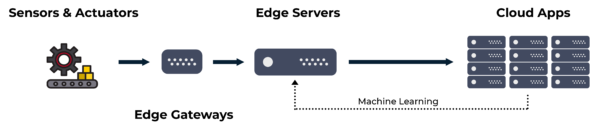
A simple manufacturing example illustrates the function of each system component. In this scenario, legacy factory-floor machines are monitored and controlled as part of smart manufacturing system, as shown below.
Edge Computing as a Service
Innovative Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers like Wasabi strategic partner Packet are introducing managed cloud-edge computing services that help customers accelerate time-to-value, achieve massive scalability and avoid edge equipment expenses and operations hassles.
These on-demand edge compute services are delivered in close proximity to customers and users, in cell towers and other far-flung locations. Cloud-edge computing services help improve the speed and scalability of bandwidth-intensive and delay-sensitive applications by eliminating WAN latency, congestion and performance bottlenecks.
Wasabi in Action
IoT and Smart System Use Cases
Companies in virtually every industry are introducing smart systems to increase automation and accelerate the pace of business. IDC projects worldwide spending on IoT technology to reach $1.2 trillion in 2022.
IoT applications include:
Manufacturing
Automated factory floor and industrial control systems, and equipment and employee monitoring and automation applications.
Transportation
connected vehicles, telematics, public transportation and traffic management applications, and commercial fleet tracking and orchestration systems.
Retail
security and loss prevention; micro-targeted shopping, marketing, customer care and advertising.
Healthcare
intelligent patient monitoring and health management applications.
Energy and utilities
smart monitoring, metering and control solutions for electricity, natural gas, oil and water distribution systems.
Inventory and logistics
intelligent warehousing, supply chain management, cargo and freight delivery, and shipping and tracking solutions.
Government and smart cities
public safety and surveillance, waste management, automated parking and toll metering, lighting, health and human services.
Agriculture
smart environmental monitoring, seeding, feeding, irrigation and harvesting control systems.
Smart buildings
HVAC, employee tracking, elevators, security and surveillance.
Wasabi Hot Cloud Storage for Smart Systems and the Internet of Things
Wasabi hot cloud storage is extremely affordable, fast and reliable cloud object storage for any purpose. Unlike first-generation cloud storage services with confusing storage tiers and complex pricing schemes, Wasabi is easy to understand and extremely cost-effective to scale.
Wasabi is perfect for storing massive datasets at the core of a smart system. You can use Wasabi as a central data repository for machine learning, business intelligence, at-rest analytics and data visualization applications, as shown below.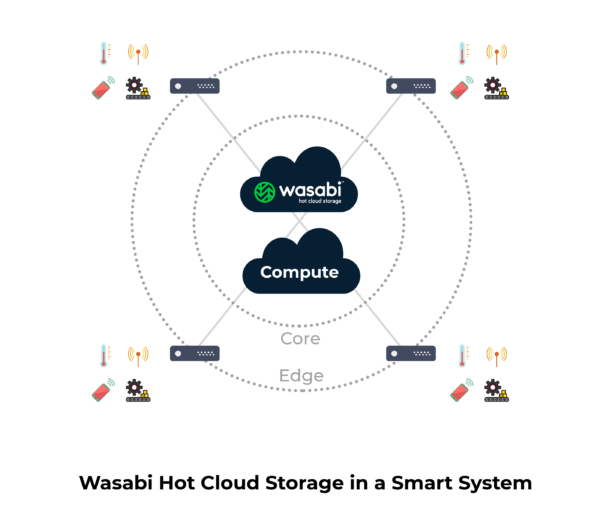
Wasabi’s key advantages for smart systems include:
Commodity pricing
Wasabi hot cloud storage costs a flat $.0059/GB/month. Compare that to $.023/GB/month for Amazon S3 Standard, $.026/GB/month for Google Multi-Regional and $.046/GB/month for Azure RA-GRS Hot.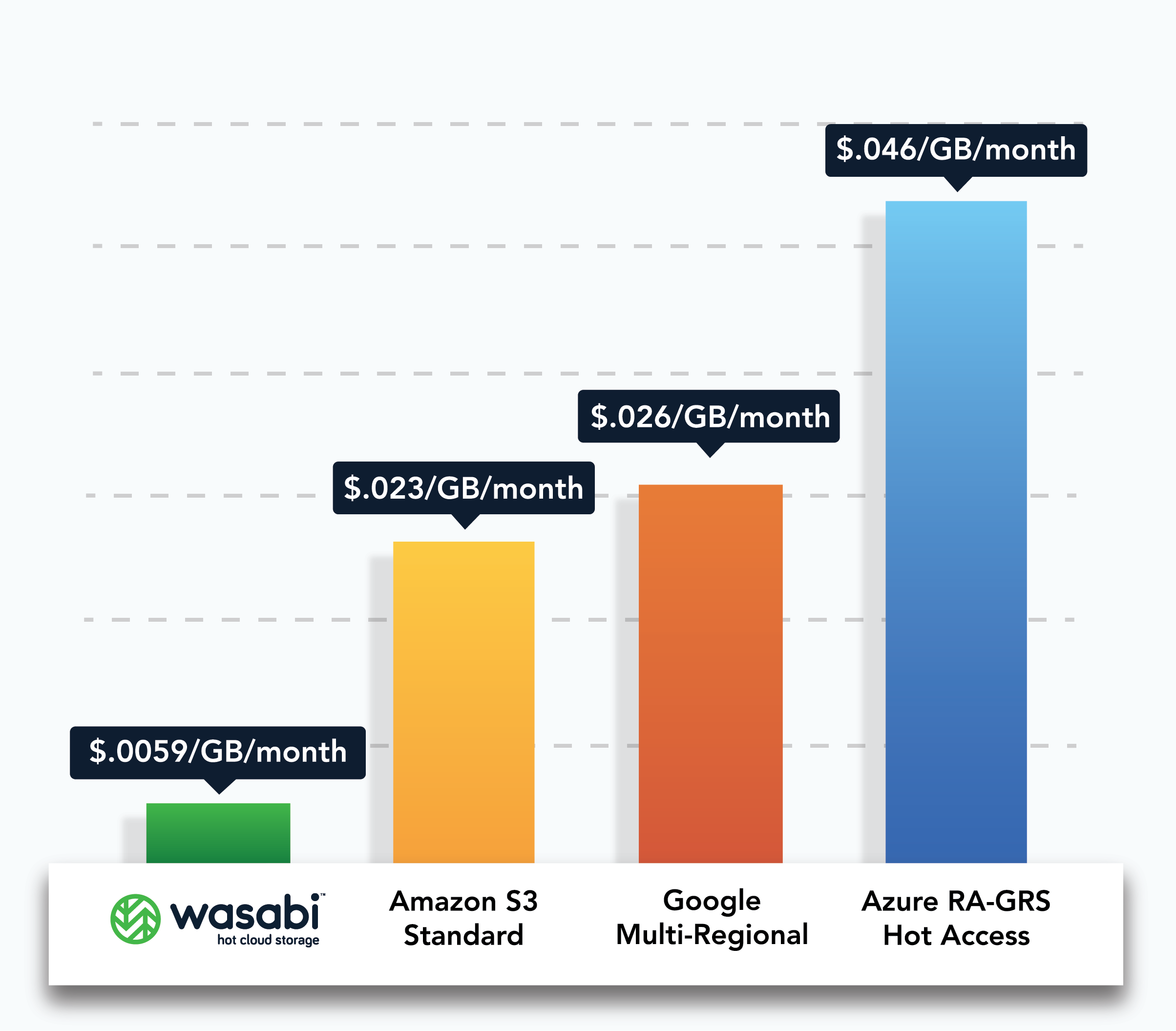
Unlike AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform we don’t impose extra fees to retrieve data from storage (egress fees). And we don’t charge extra fees for PUT, GET, DELETE or other API calls.
Read our New Economics of Cloud Storage tech brief
Superior performance Wasabi’s parallelized system architecture delivers faster read/write performances than first-generation cloud-storage services, with significantly faster time-to-first-byte speeds.
Download our Performance Benchmark report for additional information
Robust data durability and protection
Wasabi hot cloud storage is engineered to deliver extreme data durability, integrity and security. An optional data immutability capability prevents accidental deletions and administrative mishaps; protects against malware, bugs and viruses; and improves regulatory compliance.
Read our Strong Security tech brief
Read our Data Immutability tech brief
Beware of Tiered Storage Services
First-generation cloud storage providers offer confusing tiered storage services. Each storage tier is intended for a specific type of data, and has distinct performance characteristics, SLAs and pricing plans (with complex fee structures).
While each vendor’s portfolio is slightly different, these tiered services are generally optimized for three distinct classes of data.
Active Data
Live data that is readily accessible by the operating system,
an application or users. Active data is frequently accessed and has stringent read/write performance requirements.
Identifying the best storage class (and best value) for a particular application can be a real challenge with a legacy cloud storage provider. Microsoft Azure, for example, offers four distinct object storage options: General Purpose v1, General Purpose v2, Blob Storage and Premium Blob Storage. Each option has unique pricing and performance characteristics. And some (but not all) of the options support three distinct storage tiers, with distinct SLAs and fees: hot storage (for frequently accessed data), cool storage (for infrequently accessed data) and archive storage (for rarely accessed data). With so many choices and pricing variables, it is nearly impossible to make a well-informed decision and to accurately budget expenses.
At Wasabi, we believe cloud storage should be simple. Unlike legacy cloud storage services with confusing storage tiers and convoluted pricing schemes, we provide a single product—with predictable, affordable and straightforward pricing—that satisfies any cloud storage requirement. You can use Wasabi for any data storage class: active data, active archive and inactive archive.
Active Archive
Occasionally accessed data that is available instantly online
(not restored and rehydrated from an offline or remote source). Examples include backup data for rapid disaster recovery or large video files that might be accessed from time-to-time on short notice.
Inactive Archive
Infrequently accessed data. Examples include data maintained
long-term for regulatory compliance. Historically, inactive data is archived to tape and stored offsite.
Connect to Your Cloud
Wasabi has the ability to connect to your cloud applications running in AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform via the direct connect services offered by those providers (i.e. AWS Direct Connect). This range of connectivity options is enabled by Wasabi's strong partnerships with leading data center and exchange providers including Equinix, Flexential, Megaport, Digital Realty, and Iron Mountain. These private network connections avoid internet latency and bottlenecks, providing fast and predictable performance. You can also connect your private enterprise network or private cloud directly to Wasabi. Unlike with legacy cloud providers, with Wasabi Direct Connect you never pay extra transfer (egress) fees to move data out of Wasabi.
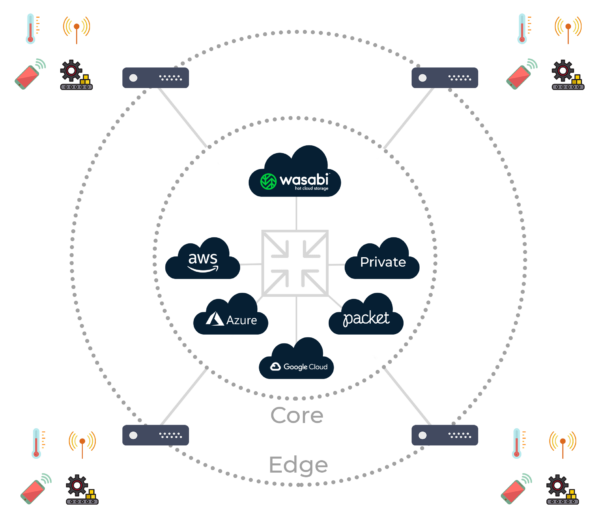
Wasabi Direct Connects to Public and Private Compute Clouds
Contact Sales
What if you could store ALL of your data in the cloud affordably?
NOW YOU CAN. Wasabi is here to guide you through your migration to the enterprise cloud and to work with you to determine which cloud storage strategy is right for your organization.